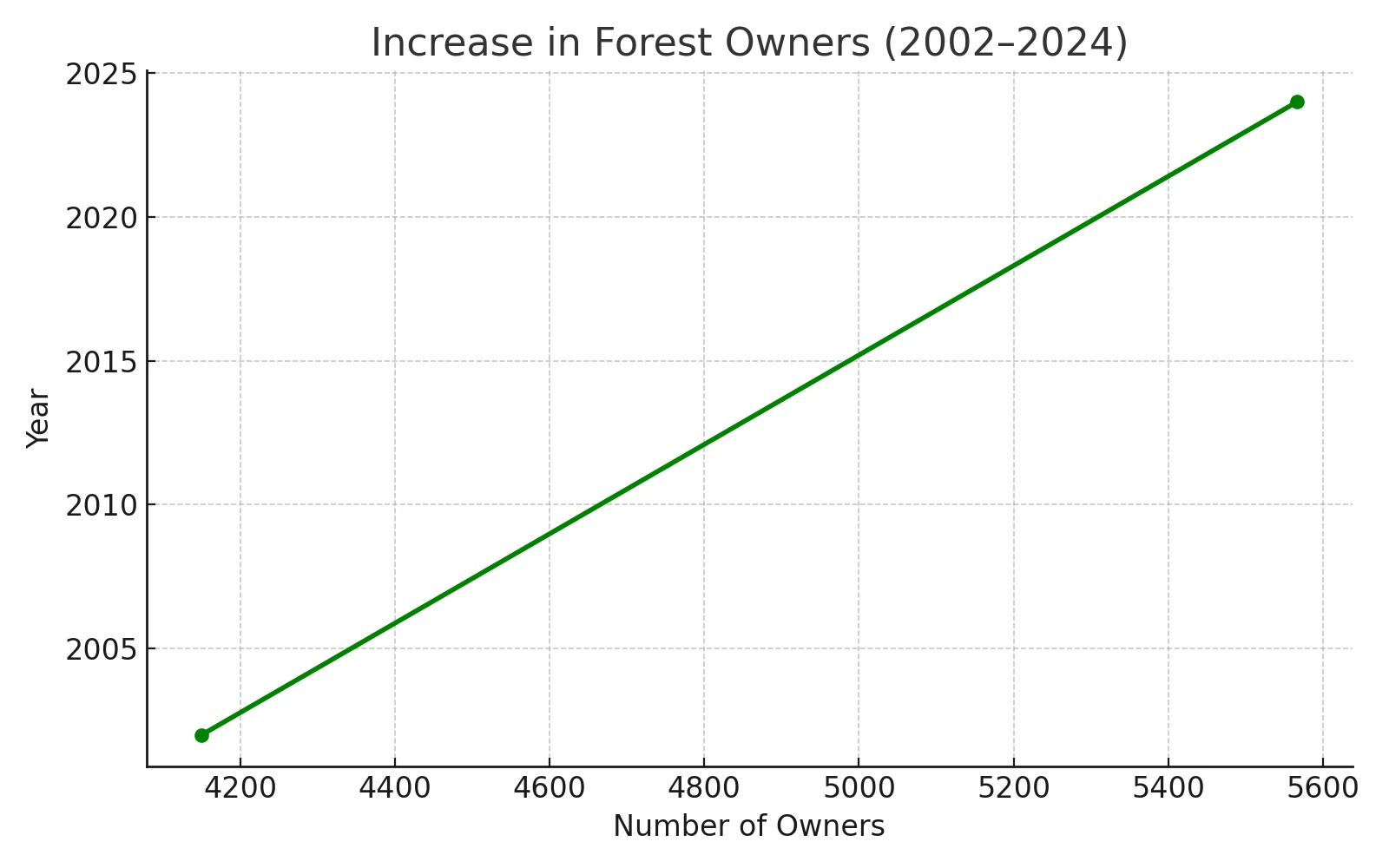
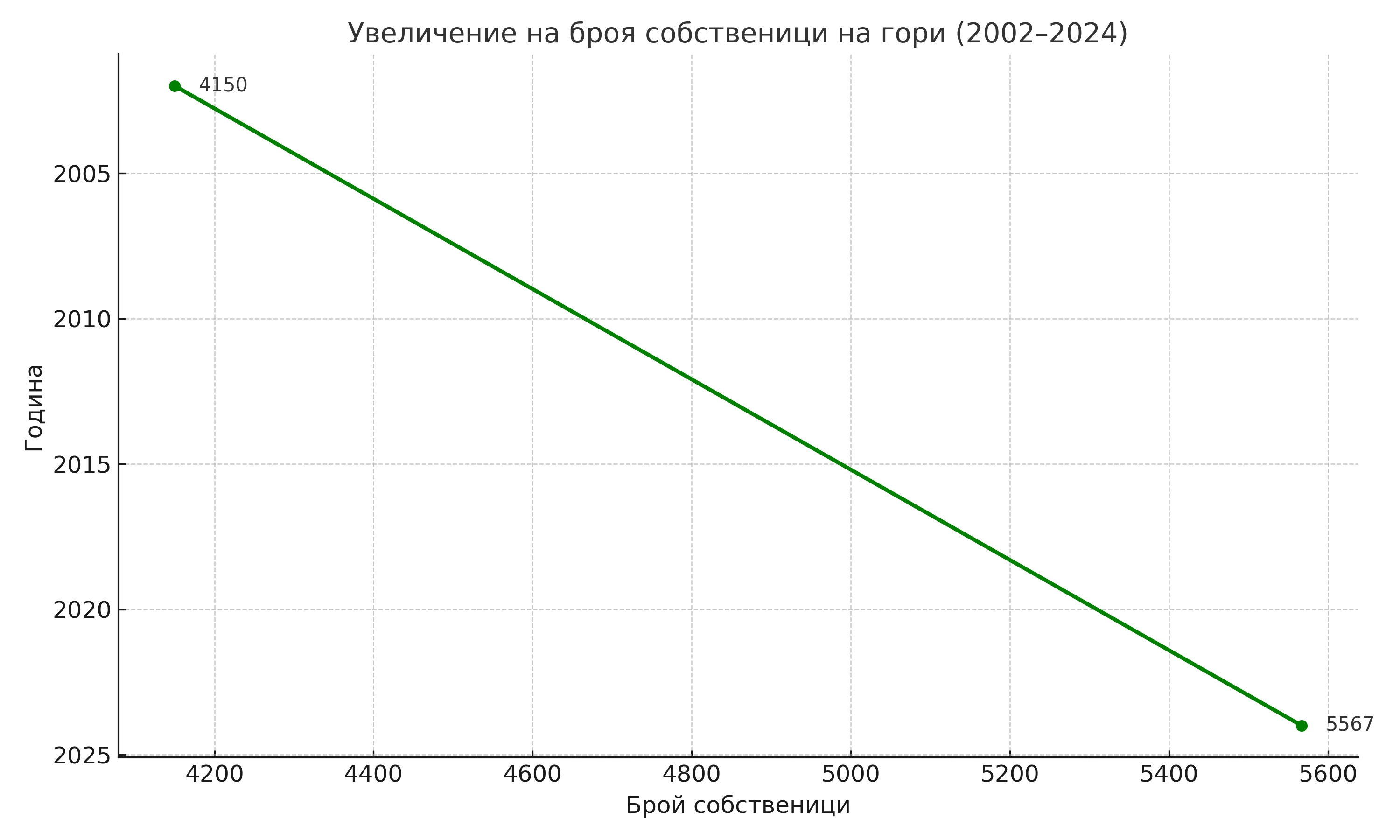
The problem of fragmentation of ownership in forests is not a recent phenomenon. Excessive fragmentation of forest properties leads to an increase in the number and area of ownerless forests, forests that are abandoned. Left without care, forests become victims of forest fires, insect attacks, winds and snow.Fragmentation is a process in which the number of owners per unit area increases and the size of the property decreases accordingly. As a result of this process, the situation is reached when the property is so small that it is of no interest to the owner himself.The smaller a forest area is, the smaller its economic value falls, and this causes the owners of forests under one or two hectares to abandon them and not take care of their property. In Bulgaria, as well as in Europe, a number of restrictions are applied to forest properties, which have become more severe over the years. This turns forest ownership into one of the most undesirable types of property.The trends of population migration to large cities, far from rural and mountainous areas, should not be underestimated. Forests are abandoned due to the physical impossibility of managing them from a distance, lack of desire on the part of the owners, due to ignorance of this matter, and last but not least, a large part of the owners simply do not know that they have inherited a given forest after the death of a grandmother, grandfather or other relative.In many cases, the value of the forest is many times less than the value of the transaction with such type of property, regardless of whether it is a purchase - sale, donation or other form of transaction. The problem is especially great with forests in joint ownership. Such are all forest cooperatives, associations and districts. The legal practice is for the transaction to be formed in all cadastral units covering the cooperative, and this makes the notarial deed unnecessarily and extremely long and expensive.In the absence of care for a forest, the forest itself and its inhabitants suffer first. Then the owner himself and the entire society lose. The state also loses from unpaid taxes on business activities.When a forest is left without an owner, it is exposed to a much greater risk of fires, in the event of an insect attack there is no one to resist and it can be more easily damaged and destroyed. It often becomes a focus for the development and spread of pests.In agricultural properties, there is an active trend of consolidation - the unification of properties by investors for the purpose of easier and more profitable processing. In forests, this is not the case at all.In conclusion, I can mention that the main problem for good forest management is the effect of fragmentation, and this is a lack of care.In the following graph, I will show how in just over 20 years the number of owners in several forest cooperatives has increased and the area of the property has decreased accordingly. Although the average area owned by a given owner is decreasing, it should be borne in mind that these forests are well managed and are not ownerless. This is not the case at all in private forests within real boundaries, which are mostly abandoned.Area of the 5 cooperatives – 2167 ha.Total number of owners as of 2002 – 4150Total number of owners by the end of 2024 – 5567Average ownership per owner by 2002 – 0.52 ha.and average by the end of 2024 – 0.39 ha.SMURF project website https://www.smurfproject.eu/.Funded by EU ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() #smurfproject #SmallForestHoldings #forestry #forestowners #profitability #smallforestowners #foresteufuture #forestmanagement #sustainability #forestnews #cascadefunding #closetonaturesilvicultureSee translation
#smurfproject #SmallForestHoldings #forestry #forestowners #profitability #smallforestowners #foresteufuture #forestmanagement #sustainability #forestnews #cascadefunding #closetonaturesilvicultureSee translation